# 1. 需求背景
随着人工智能技术的快速发展,基于 LLM 的对话系统已广泛应用于教育、医疗、政务和企业服务等领域。然而,当前大多数 AI 系统仍存在一个突出问题:记忆能力有限。在长时间的交互过程中,系统往往无法有效保留先前的信息,容易遗忘用户已提供的关键事实,从而出现重复提问、逻辑断裂甚至错误回答的情况。这种缺陷直接影响了用户体验,也限制了 AI 在复杂任务和长期陪伴场景中的应用价值。
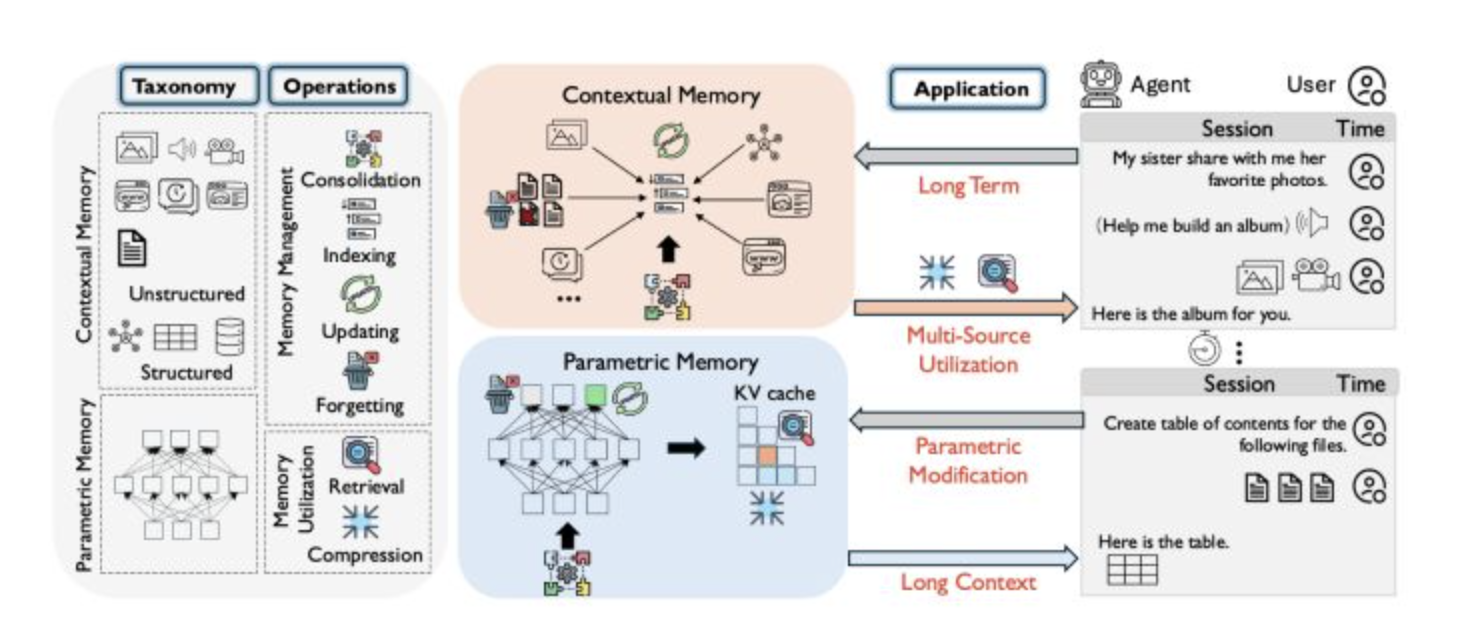
针对这一问题,研究者提出了新的记忆架构 Mem0。该架构能够在对话过程中动态提取并整合关键信息,使 AI 系统在不同会话之间保持连续性和一致性。相比传统依赖短期上下文的方法,Mem0 能够高效捕捉核心事实,避免无效冗余信息的积累,从而提升系统在长期对话中的表现。
在此基础上,研究者进一步提出了 Mem0g。Mem0g 将图结构记忆(知识图谱)引入到 Mem0 框架中,使系统能够以实体和关系为核心进行知识存储与检索。这种增强方式不仅提升了信息的组织性与可追溯性,还使 AI 在面对复杂关系推理、多跳问答和开放域知识整合时更加得心应手,从而拓展了其在智能问答、决策支持和知识管理等场景中的应用潜力。
# 2. Mem0基本介绍
# 2.1 Mem0项目简介
Mem0 是一个为大语言模型(LLMs)设计的可扩展记忆层框架,旨在突破固定上下文窗口的限制,提升多轮对话的一致性和个性化体验。它通过动态提取、整合和检索对话中的关键信息,使 AI 能够在长期、多会话场景中保持稳定的推理能力和上下文连贯性。
- 项目地址:https://github.com/mem0ai/mem0 (opens new window)
- 官方文档:https://docs.mem0.ai/introduction (opens new window)
- 研究论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.19413 (opens new window)
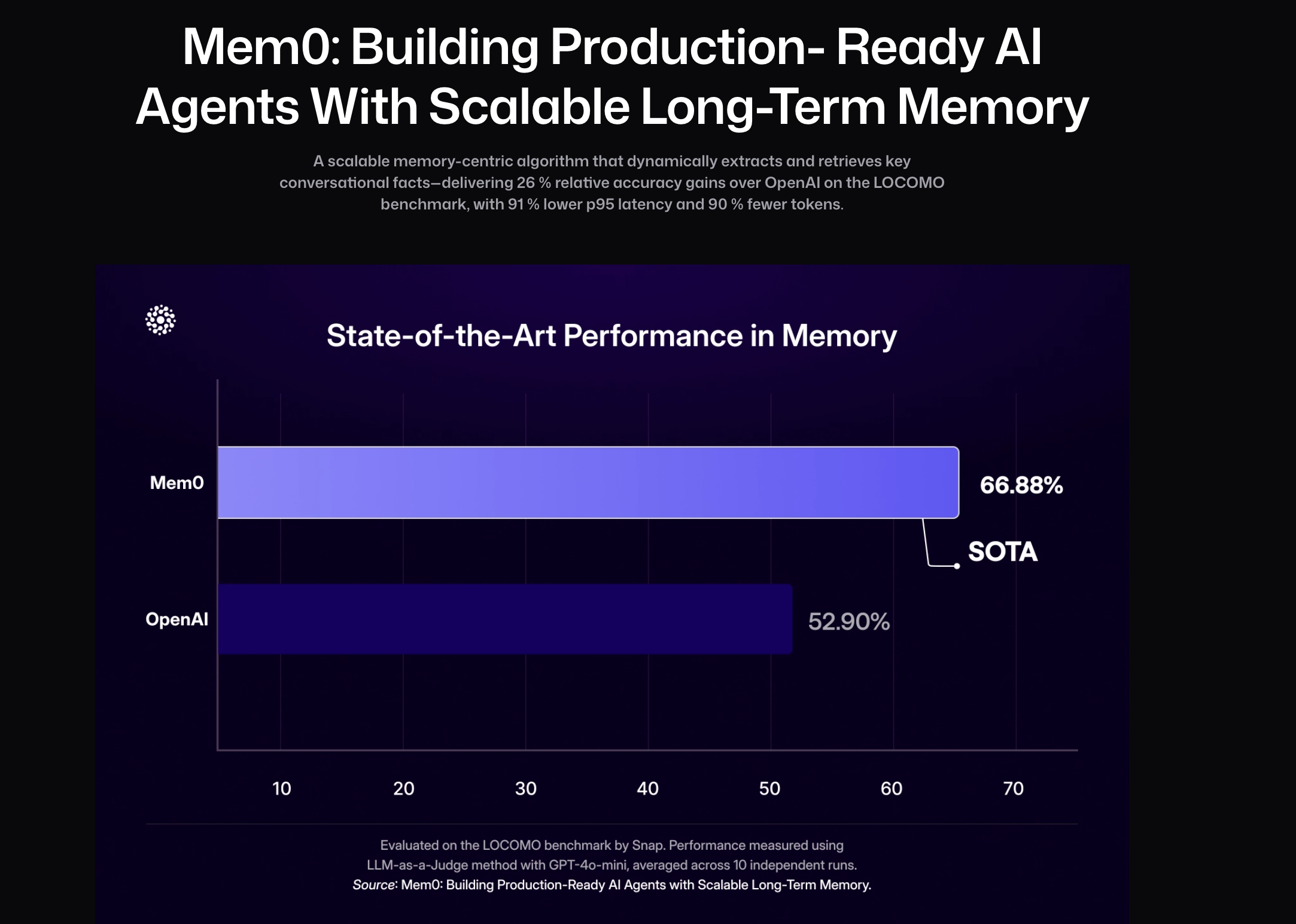
在最新研究中,Mem0 展现出在记忆效果与计算效率上的双重优势。它通过可扩展的记忆架构,动态提取、整合并检索长对话中的关键信息,从根本上解决了 LLM 在多轮交互中的遗忘问题。
相比全上下文方法,Mem0 在 LOCOMO 基准上实现了 p95 延迟降低 91%、Token 成本节省超过 90% 的显著优化,同时在记忆精度上较 OpenAI 提升 26%。进一步的增强版本 Mem0g 引入图结构记忆,能够捕捉跨会话的复杂关系,提升多跳推理与开放域问答的表现。通过这一系列改进,Mem0 让持久化、结构化的记忆真正实现规模化应用,为 AI 提供长期一致性、适应性与协作能力。
# 2.2 Mem0架构技术原理
Mem0 的架构核心在于记忆提取与记忆更新机制,旨在确保 AI 系统能够动态地提取对话中的关键信息,并有效地更新其记忆库。
- 在记忆提取阶段,系统结合最新对话、滚动摘要和最近消息,由 LLM 抽取简洁候选记忆,并异步刷新长时摘要以降低延迟;
- 在记忆更新阶段,新事实与向量库中相似记忆比对后,由 LLM 判断是新增、更新、删除还是保持不变,从而保证记忆库相关、无冗余且随时可用。
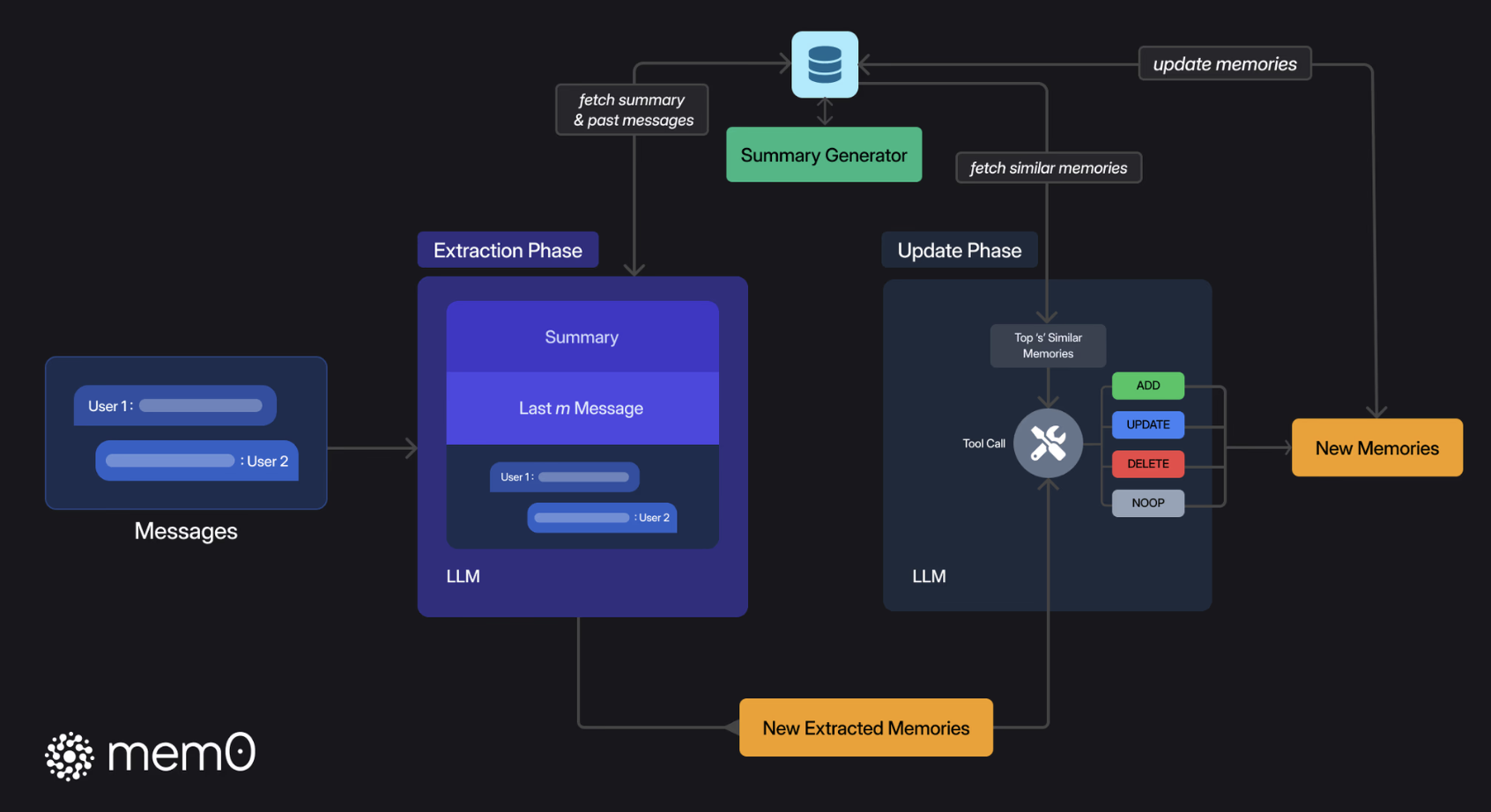
# 2.2.1 Mem0记忆提取
首先,当新的对话消息进入系统后,Mem0会通过一个异步摘要生成模块生成并存储一个会话摘要(S)。它的作用是概括整个对话的核心主题,从而为后续的记忆提取提供全局记忆。这个过程并不是一次性的,而是随着对话的进展持续进行更新。
# mem0/memory/main.py - 记忆提取部分
def _create_procedural_memory(self, messages, metadata=None, prompt=None):
"""
# 异步摘要生成模块:创建程序化记忆(会话摘要)
# 该函数接收对话消息,使用LLM生成一个摘要,并将其存储为特殊类型的记忆
Args:
messages (list): 待处理的对话消息列表
metadata (dict): 存储元数据信息
prompt (str, optional): 自定义提示词,默认使用系统提示
"""
logger.info("Creating procedural memory")
# 1. 构建系统提示和用户消息,用于指导LLM生成摘要
parsed_messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": prompt or PROCEDURAL_MEMORY_SYSTEM_PROMPT},
*messages,
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Create procedural memory of the above conversation.",
},
]
try:
# 2. 使用LLM生成对话的摘要记忆
procedural_memory = self.llm.generate_response(messages=parsed_messages)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error generating procedural memory summary: {e}")
raise
if metadata is None:
raise ValueError("Metadata cannot be done for procedural memory.")
# 3. 标记这是一个程序化记忆(会话摘要)
metadata["memory_type"] = MemoryType.PROCEDURAL.value
# 4. 为摘要生成向量嵌入
embeddings = self.embedding_model.embed(procedural_memory, memory_action="add")
# 5. 创建记忆并存储在向量数据库中
memory_id = self._create_memory(procedural_memory, {procedural_memory: embeddings}, metadata=metadata)
capture_event("mem0._create_procedural_memory", self, {"memory_id": memory_id, "sync_type": "sync"})
# 6. 返回创建的记忆结果
result = {"results": [{"id": memory_id, "memory": procedural_memory, "event": "ADD"}]}
return result
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
这里使用的 PROCEDURAL_MEMORY_SYSTEM_PROMPT 很长,很多 Agent 的 Prompt 都是结构化的长文本,说明 Prompt Engineering 是很重要的。
PROCEDURAL_MEMORY_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
You are a memory summarization system that records and preserves the complete interaction history between a human and an AI agent. You are provided with the agent’s execution history over the past N steps. Your task is to produce a comprehensive summary of the agent's output history that contains every detail necessary for the agent to continue the task without ambiguity. **Every output produced by the agent must be recorded verbatim as part of the summary.**
### Overall Structure:
- **Overview (Global Metadata):**
- **Task Objective**: The overall goal the agent is working to accomplish.
- **Progress Status**: The current completion percentage and summary of specific milestones or steps completed.
- **Sequential Agent Actions (Numbered Steps):**
Each numbered step must be a self-contained entry that includes all of the following elements:
1. **Agent Action**:
- Precisely describe what the agent did (e.g., "Clicked on the 'Blog' link", "Called API to fetch content", "Scraped page data").
- Include all parameters, target elements, or methods involved.
2. **Action Result (Mandatory, Unmodified)**:
- Immediately follow the agent action with its exact, unaltered output.
- Record all returned data, responses, HTML snippets, JSON content, or error messages exactly as received. This is critical for constructing the final output later.
3. **Embedded Metadata**:
For the same numbered step, include additional context such as:
- **Key Findings**: Any important information discovered (e.g., URLs, data points, search results).
- **Navigation History**: For browser agents, detail which pages were visited, including their URLs and relevance.
- **Errors & Challenges**: Document any error messages, exceptions, or challenges encountered along with any attempted recovery or troubleshooting.
- **Current Context**: Describe the state after the action (e.g., "Agent is on the blog detail page" or "JSON data stored for further processing") and what the agent plans to do next.
### Guidelines:
1. **Preserve Every Output**: The exact output of each agent action is essential. Do not paraphrase or summarize the output. It must be stored as is for later use.
2. **Chronological Order**: Number the agent actions sequentially in the order they occurred. Each numbered step is a complete record of that action.
3. **Detail and Precision**:
- Use exact data: Include URLs, element indexes, error messages, JSON responses, and any other concrete values.
- Preserve numeric counts and metrics (e.g., "3 out of 5 items processed").
- For any errors, include the full error message and, if applicable, the stack trace or cause.
4. **Output Only the Summary**: The final output must consist solely of the structured summary with no additional commentary or preamble.
### Example Template:
/```
## Summary of the agent's execution history
**Task Objective**: Scrape blog post titles and full content from the OpenAI blog.
**Progress Status**: 10/%/ complete — 5 out of 50 blog posts processed.
1. **Agent Action**: Opened URL "https://openai.com"
**Action Result**:
"HTML Content of the homepage including navigation bar with links: 'Blog', 'API', 'ChatGPT', etc."
**Key Findings**: Navigation bar loaded correctly.
**Navigation History**: Visited homepage: "https://openai.com"
**Current Context**: Homepage loaded; ready to click on the 'Blog' link.
2. **Agent Action**: Clicked on the "Blog" link in the navigation bar.
**Action Result**:
"Navigated to 'https://openai.com/blog/' with the blog listing fully rendered."
**Key Findings**: Blog listing shows 10 blog previews.
**Navigation History**: Transitioned from homepage to blog listing page.
**Current Context**: Blog listing page displayed.
3. **Agent Action**: Extracted the first 5 blog post links from the blog listing page.
**Action Result**:
"[ '/blog/chatgpt-updates', '/blog/ai-and-education', '/blog/openai-api-announcement', '/blog/gpt-4-release', '/blog/safety-and-alignment' ]"
**Key Findings**: Identified 5 valid blog post URLs.
**Current Context**: URLs stored in memory for further processing.
4. **Agent Action**: Visited URL "https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt-updates"
**Action Result**:
"HTML content loaded for the blog post including full article text."
**Key Findings**: Extracted blog title "ChatGPT Updates – March 2025" and article content excerpt.
**Current Context**: Blog post content extracted and stored.
5. **Agent Action**: Extracted blog title and full article content from "https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt-updates"
**Action Result**:
"{ 'title': 'ChatGPT Updates – March 2025', 'content': 'We\'re introducing new updates to ChatGPT, including improved browsing capabilities and memory recall... (full content)' }"
**Key Findings**: Full content captured for later summarization.
**Current Context**: Data stored; ready to proceed to next blog post.
... (Additional numbered steps for subsequent actions)
/```
"""
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
当有新的对话消息进入系统时,Mem0 会从数据库中取出本次对话的会话摘要(S),帮助系统理解整个对话的全局上下文。 此外,Mem0 还会使用一个最近消息窗口,即最近的若干条消息(由超参数 m 控制),以便提取出更多的细节上下文信息。
Mem0 会将会话摘要和最近消息结合起来(很常见的全局和局部信息结合的思想),与当前的新消息(用户和助手的最新一轮对话)一起,生成一个综合提示(P)。这个提示会被送入一个提取函数,通过 LLM 来处理和提取出一组候选记忆(Ω)。这些候选记忆是与当前对话相关的关键信息,用于后续更新知识库中的记忆。
# mem0/memory/main.py - 提取记忆事实的相关代码
def _add_to_vector_store(self, messages, metadata, filters, infer):
"""
提取记忆功能:处理消息并提取记忆事实
该函数实现了记忆的提取和存储过程
"""
# 如果不需要生成记忆片段,则直接存储原始消息(按原样存储)
if not infer:
returned_memories = []
for message in messages:
if message["role"] != "system":
message_embeddings = self.embedding_model.embed(message["content"], "add")
memory_id = self._create_memory(message["content"], message_embeddings, metadata)
returned_memories.append({"id": memory_id, "memory": message["content"], "event": "ADD"})
return returned_memories
# 1. 解析对话消息,形成上下文
parsed_messages = parse_messages(messages)
# 2. 构建提示,使用最近消息窗口作为上下文
if self.config.custom_fact_extraction_prompt:
system_prompt = self.config.custom_fact_extraction_prompt
user_prompt = f"Input:\n{parsed_messages}"
else:
system_prompt, user_prompt = get_fact_retrieval_messages(parsed_messages) # 提取记忆的system prompt自己看源码吧,比较长这里就不贴了
# 3. 使用LLM提取事实(候选记忆)
response = self.llm.generate_response(
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt},
],
response_format={"type": "json_object"},
)
# 4. 解析LLM输出,获取候选记忆
try:
response = remove_code_blocks(response)
new_retrieved_facts = json.loads(response)["facts"] # 候选记忆列表
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error in new_retrieved_facts: {e}")
new_retrieved_facts = []
# 5. 准备从向量数据库检索相似记忆,以便后续进行更新决策
retrieved_old_memory = []
new_message_embeddings = {}
for new_mem in new_retrieved_facts:
# 为每个候选记忆生成向量嵌入
messages_embeddings = self.embedding_model.embed(new_mem, "add")
new_message_embeddings[new_mem] = messages_embeddings
# 检索向量数据库中与候选记忆语义相似的现有记忆
existing_memories = self.vector_store.search(
query=new_mem,
vectors=messages_embeddings,
limit=5,
filters=filters,
)
# 收集相似的现有记忆
for mem in existing_memories:
retrieved_old_memory.append({"id": mem.id, "text": mem.payload["data"]})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# 2.2.2 Mem0记忆更新
记忆提取后,Mem0 会进入记忆更新阶段。在这个阶段,系统会将刚提取的候选记忆组与现有记忆进行对比,确保它们的一致性并避免冗余。为此,Mem0 首先会检索出与候选记忆语义最相似的若干个现有记忆(向量数据库向量检索)。然后通过 function call 的形式调用记忆更新工具来更新记忆。工具有4个:
- 添加(ADD):当没有语义相似的记忆时,将新记忆添加到知识库。
- 更新(UPDATE):当现有记忆与新记忆有部分重叠时,更新现有记忆,以纳入新信息。
- 删除(DELETE):当现有记忆与新记忆存在冲突时,删除旧记忆。
- 无操作(NOOP):当新记忆与现有记忆一致时,保持现有记忆不变。
当现有记忆与新提取的候选记忆存在冲突时,Mem0 会决定是否删除、更新或添加新记忆。
# mem0/memory/main.py - 记忆更新部分
# 继续_add_to_vector_store函数中的记忆更新流程...
# 使用LLM决定每个记忆的操作(添加/更新/删除/无操作)
try:
response: str = self.llm.generate_response(
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": function_calling_prompt}],
response_format={"type": "json_object"},
)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error in new memory actions response: {e}")
response = ""
# 解析LLM的决策结果
try:
response = remove_code_blocks(response)
new_memories_with_actions = json.loads(response)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Invalid JSON response: {e}")
new_memories_with_actions = {}
# 根据决策结果执行相应的记忆操作
returned_memories = []
try:
for resp in new_memories_with_actions.get("memory", []):
logging.info(resp)
try:
if not resp.get("text"):
logging.info("Skipping memory entry because of empty `text` field.")
continue
# 添加新记忆
elif resp.get("event") == "ADD":
memory_id = self._create_memory(
data=resp.get("text"),
existing_embeddings=new_message_embeddings,
metadata=deepcopy(metadata),
)
returned_memories.append(
{
"id": memory_id,
"memory": resp.get("text"),
"event": resp.get("event"),
}
)
# 更新现有记忆
elif resp.get("event") == "UPDATE":
self._update_memory(
memory_id=temp_uuid_mapping[resp["id"]],
data=resp.get("text"),
existing_embeddings=new_message_embeddings,
metadata=deepcopy(metadata),
)
returned_memories.append(
{
"id": temp_uuid_mapping[resp.get("id")],
"memory": resp.get("text"),
"event": resp.get("event"),
"previous_memory": resp.get("old_memory"),
}
)
# 删除现有记忆
elif resp.get("event") == "DELETE":
self._delete_memory(memory_id=temp_uuid_mapping[resp.get("id")])
returned_memories.append(
{
"id": temp_uuid_mapping[resp.get("id")],
"memory": resp.get("text"),
"event": resp.get("event"),
}
)
# 无需操作
elif resp.get("event") == "NONE":
logging.info("NOOP for Memory.")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error in new_memories_with_actions: {e}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error in new_memories_with_actions: {e}")
return returned_memories
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
这一机制的核心在于保持记忆库的一致性并且避免冗余信息。
保存好记忆后,检索就方便了,直接向量数据库语义相似度取top-k个最相似的记忆即可。
# mem0/memory/main.py - 会话摘要检索部分
def search(self, query, user_id=None, agent_id=None, run_id=None, limit=100, filters=None):
"""
搜索记忆函数:从记忆库中搜索相关信息
该函数会搜索包括会话摘要在内的各类记忆
Args:
query (str): 搜索查询内容
user_id, agent_id, run_id: 用于过滤的ID
limit: 结果数量上限
filters: 额外的过滤条件
"""
filters = filters or {}
if user_id:
filters["user_id"] = user_id
if agent_id:
filters["agent_id"] = agent_id
if run_id:
filters["run_id"] = run_id
if not any(key in filters for key in ("user_id", "agent_id", "run_id")):
raise ValueError("One of the filters: user_id, agent_id or run_id is required!")
capture_event(
"mem0.search",
self,
{"limit": limit, "version": self.api_version, "keys": list(filters.keys()), "sync_type": "sync"},
)
# 将向量存储和图存储的搜索并行执行以提高效率
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor:
# 1. 从向量数据库中搜索记忆(包括会话摘要)
future_memories = executor.submit(self._search_vector_store, query, filters, limit)
# 2. 如果启用了图存储,同时在图中搜索
future_graph_entities = (
executor.submit(self.graph.search, query, filters, limit) if self.enable_graph else None
)
concurrent.futures.wait(
[future_memories, future_graph_entities] if future_graph_entities else [future_memories]
)
# 获取搜索结果
original_memories = future_memories.result()
graph_entities = future_graph_entities.result() if future_graph_entities else None
# 返回搜索结果,包括会话摘要和其他记忆
if self.enable_graph:
return {"results": original_memories, "relations": graph_entities}
# API版本兼容处理
if self.api_version == "v1.0":
warnings.warn(
"The current get_all API output format is deprecated. "
"To use the latest format, set `api_version='v1.1'`. "
"The current format will be removed in mem0ai 1.1.0 and later versions.",
category=DeprecationWarning,
stacklevel=2,
)
return original_memories
else:
return {"results": original_memories}
def _search_vector_store(self, query, filters, limit):
"""
向量存储搜索功能:基于语义相似度搜索记忆
该函数实现了实际的向量检索逻辑
"""
# 1. 将查询转换为向量表示
embeddings = self.embedding_model.embed(query, "search")
# 2. 在向量数据库中搜索相似的记忆,包括会话摘要
memories = self.vector_store.search(query=query, vectors=embeddings, limit=limit, filters=filters)
# 需要排除的元数据键
excluded_keys = {
"user_id",
"agent_id",
"run_id",
"hash",
"data",
"created_at",
"updated_at",
"id",
}
# 3. 格式化搜索结果,包含相似度分数
original_memories = [
{
**MemoryItem(
id=mem.id,
memory=mem.payload["data"],
hash=mem.payload.get("hash"),
created_at=mem.payload.get("created_at"),
updated_at=mem.payload.get("updated_at"),
score=mem.score, # 包含相似度分数
).model_dump(),
**{key: mem.payload[key] for key in ["user_id", "agent_id", "run_id"] if key in mem.payload},
**(
{"metadata": {k: v for k, v in mem.payload.items() if k not in excluded_keys}}
if any(k for k in mem.payload if k not in excluded_keys)
else {}
),
}
for mem in memories
]
return original_memories
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
# 2.3 Mem0g架构工作原理
Mem0g 将记忆组织为有向标注图。
- 在记忆提取阶段,它从输入消息中抽取实体作为节点,并生成关系作为边,从而把文本转化为结构化图谱。
- 在记忆更新阶段,系统检测冲突或冗余,由 LLM 决定增添、合并、作废或跳过图元素。最终形成的知识图支持子图检索与语义三元组匹配,提升多跳推理、时间推理和开放域推理的能力。
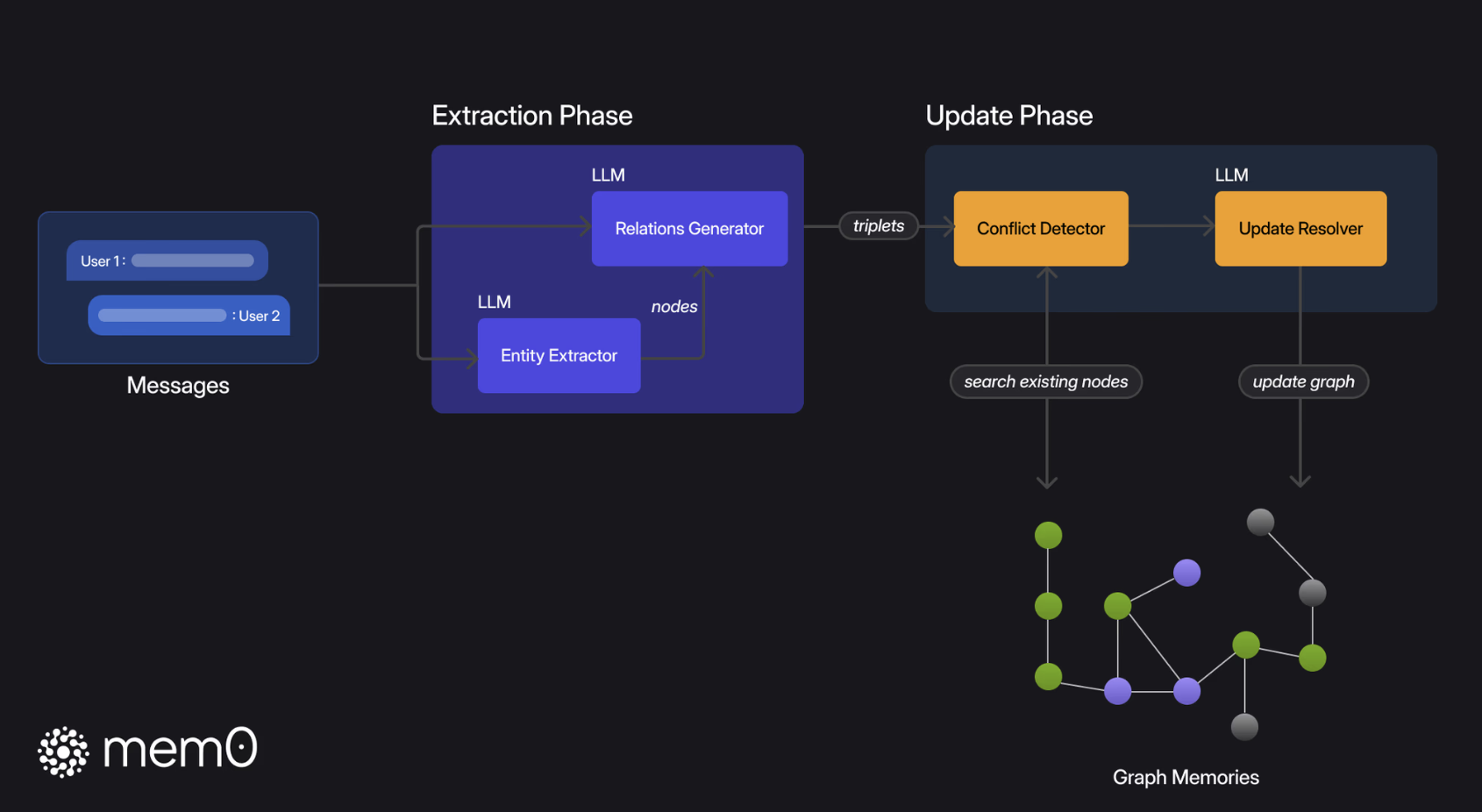
# 2.3.1 Mem0g记忆提取
Mem0g 采用图结构来表示和管理对话中的实体与关系。它首先通过实体提取模块识别对话中的关键实体(如人物、地点、事件等)及其类别;随后,关系生成模块会结合上下文,为这些实体之间建立联系,从而形成一组三元组(实体 A、实体 B、关系 R)。这些三元组共同构成了记忆知识图谱。
与传统 NLP 时代(BERT 及其衍生方法)常见的一步法不同,Mem0g 采用了大模型结合提示词(Prompt)的方式,并将过程拆分为两个阶段:先进行实体抽取,再生成实体间的关系。传统方法中虽然也有直接一步同时抽取实体和关系的方案,但 Mem0g 更注重通过分阶段设计来保证信息抽取的准确性和灵活性。
# mem0/memory/graph_memory.py - 知识图谱记忆模块
class MemoryGraph:
def __init__(self, config: MemoryConfig = MemoryConfig()):
"""
知识图谱记忆模块初始化
负责实体提取、关系生成和图谱维护
"""
self.config = config
# 初始化图数据库存储
self.graph_store = GraphStoreFactory.create(
self.config.graph_store.provider, self.config.graph_store.config
)
# 初始化LLM用于实体和关系提取
self.llm = LlmFactory.create(self.config.llm.provider, self.config.llm.config)
# 初始化嵌入模型用于语义相似度计算
self.embedding_model = EmbedderFactory.create(
self.config.embedder.provider,
self.config.embedder.config,
self.config.vector_store.config,
)
def add(self, message, filters=None):
"""
向知识图谱添加新信息
实现从文本中提取实体和关系并构建知识图谱
"""
filters = filters or {}
# 1. 使用LLM提取实体
# 实体提取模块:从文本中识别相关实体及其类别
entity_prompt = self._get_entity_extraction_prompt(message)
entity_response = self.llm.generate_response(
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": entity_prompt}],
response_format={"type": "json_object"},
)
try:
# 解析LLM返回的实体列表
entity_response = remove_code_blocks(entity_response)
entity_data = json.loads(entity_response)
entities = entity_data.get("entities", [])
# 如果没有提取到实体,直接返回
if not entities:
return []
# 2. 使用LLM生成实体间关系
# 关系生成模块:根据上下文建立实体之间的语义关系
relation_prompt = self._get_relation_extraction_prompt(message, entities)
relation_response = self.llm.generate_response( # 核心还是构建prompt+调用大模型的方式
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": relation_prompt}],
response_format={"type": "json_object"},
)
# 解析LLM返回的关系列表
relation_response = remove_code_blocks(relation_response)
relation_data = json.loads(relation_response)
relations = relation_data.get("relations", [])
# 3. 将实体和关系添加到图数据库中
added_entities = []
for relation in relations:
# 处理头实体
source_entity = relation.get("source")
source_entity_type = relation.get("source_type")
# 处理尾实体
target_entity = relation.get("target")
target_entity_type = relation.get("target_type")
# 处理关系
relationship = relation.get("relationship")
# 将实体和关系信息添加到图数据库
if source_entity and target_entity and relationship:
# 为实体和关系生成向量嵌入,用于后续相似性检索
source_entity_embeddings = self.embedding_model.embed(source_entity, "add")
target_entity_embeddings = self.embedding_model.embed(target_entity, "add")
# 添加到图数据库并记录结果
result = self.graph_store.add_triple(
source=source_entity,
source_type=source_entity_type,
relationship=relationship,
target=target_entity,
target_type=target_entity_type,
source_embedding=source_entity_embeddings,
target_embedding=target_entity_embeddings,
metadata=filters
)
added_entities.append({
"source": source_entity,
"source_type": source_entity_type,
"relationship": relationship,
"destination": target_entity,
"destination_type": target_entity_type
})
return added_entities
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error in entity/relation extraction: {e}")
return []
def _get_entity_extraction_prompt(self, message):
"""
生成实体提取的提示词
指导LLM识别文本中的各类实体
"""
return """You are an entity extraction system. Your task is to identify the most important entities in the given text.
An entity can be a person, place, organization, product, or concept. For each entity, provide its type.
Format your response as a JSON object with a single key "entities", containing a list of entity objects.
Each entity object should have "name" (the entity) and "type" fields.
Here is the text to analyze:
/```
{message}
/```
JSON Response:
""".format(message=message)
def _get_relation_extraction_prompt(self, message, entities):
"""
生成关系提取的提示词
指导LLM识别已提取实体之间的关系
"""
entity_names = [e.get("name") for e in entities]
entity_str = ", ".join(entity_names)
return """You are a relationship extraction system. Your task is to identify meaningful relationships between the entities in the given text.
Text:
/```
{message}
/```
Entities: {entities}
For each relationship you identify, specify:
1. The source entity
2. The type of the source entity
3. The relationship (a verb or phrase describing how entities are connected)
4. The target entity
5. The type of the target entity
Only create relationships that are explicitly or strongly implied in the text.
Format your response as a JSON object with a single key "relations", containing a list of relationship objects.
JSON Response:
""".format(message=message, entities=entity_str)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
# 2.3.2 Mem0g记忆更新
Mem0g 通过 Neo4j 图数据库实现节点和边的检索。具体来说,Mem0g 会计算新提取的实体与现有节点之间的语义相似度,并根据阈值决定是否更新或添加新的节点和关系。对图的操作(其实就是修改数据库中的三元组信息)也是通过 function call 的形式完成,具体 tool和 Mem0 类似:
- 添加(ADD):当新信息对应的实体和关系在图中没有对应节点时,Mem0g 会创建新的节点并建立关系。
- 更新(UPDATE):当现有图中的节点与新信息重合时,Mem0g 会通过更新节点属性(时间戳)来增强现有记忆。
- 删除(DELETE):如果新提取的信息与现有关系发生冲突,Mem0g 会删除这些冲突的关系,确保图结构的一致性。
- 无操作(NOOP):如果新信息与现有记忆一致,则不做任何操作,避免不必要的更新。
Mem0g 的记忆检索机制与 Mem0 有明显差异,它在处理查询时引入了双重检索策略。
- 一方面是基于实体的检索:系统会先识别查询中的核心实体,在图结构中定位到对应的节点,然后沿着这些节点展开,探索它们的关联关系以及相关的尾实体,从而捕捉上下文中的实体链条。
- 另一方面是语义三元组检索:系统会将整个查询转化为向量表示,再与图中的三元组表示进行匹配,以捕捉语义层面的潜在联系。
这两种检索方式并行叠加,使得 Mem0g 能在实体关联和语义匹配两个维度上同时展开搜索,从而获取更全面、更精确的记忆信息。
# mem0/memory/graph_memory.py - 知识图谱记忆检索功能
def search(self, query, filters=None, limit=20):
"""
图谱记忆检索功能
实现双重检索策略:基于实体检索 + 语义三元组检索
Args:
query: 用户查询文本
filters: 过滤条件
limit: 返回结果数量限制
"""
filters = filters or {}
results = []
try:
# 1. 基于实体的检索策略
# 首先识别查询中的实体,然后在图中查找这些实体的关系
# 1.1 从查询中提取实体
entity_prompt = self._get_entity_extraction_prompt(query)
entity_response = self.llm.generate_response(
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": entity_prompt}],
response_format={"type": "json_object"},
)
entity_response = remove_code_blocks(entity_response)
entity_data = json.loads(entity_response)
entities = entity_data.get("entities", [])
# 1.2 如果查询中有实体,在图中检索相关实体和关系
if entities:
entity_names = [e.get("name") for e in entities]
# 以并行方式为每个实体检索关联关系
for entity_name in entity_names:
# 查找该实体作为源节点的关系
source_relations = self.graph_store.search_by_source(
source=entity_name,
metadata=filters,
limit=limit
)
# 查找该实体作为目标节点的关系
target_relations = self.graph_store.search_by_target(
target=entity_name,
metadata=filters,
limit=limit
)
# 合并关系结果
entity_relations = source_relations + target_relations
results.extend(entity_relations)
# 2. 语义三元组检索策略
# 将查询转换为向量,然后在图中查找语义相似的三元组
# 2.1 为查询生成向量嵌入
query_embedding = self.embedding_model.embed(query, "search")
# 2.2 在图中进行语义相似度搜索
semantic_results = self.graph_store.search_by_vector(
vector=query_embedding,
metadata=filters,
limit=limit
)
# 将语义搜索结果添加到最终结果中
results.extend(semantic_results)
# 3. 结果去重和格式化
# 由于两种检索策略可能返回重复的三元组,需要去重
unique_results = []
seen_ids = set()
for result in results:
# 生成唯一标识,避免重复
result_id = f"{result.get('source')}-{result.get('relationship')}-{result.get('target')}"
if result_id not in seen_ids:
seen_ids.add(result_id)
# 格式化结果
formatted_result = {
"source": result.get("source"),
"source_type": result.get("source_type"),
"relationship": result.get("relationship"),
"destination": result.get("target"),
"destination_type": result.get("target_type"),
"confidence": result.get("score", 1.0) if "score" in result else 1.0
}
unique_results.append(formatted_result)
# 根据相似度或置信度排序结果
unique_results.sort(key=lambda x: x.get("confidence", 0), reverse=True)
# 限制返回结果数量
return unique_results[:limit]
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error in graph memory search: {e}")
return []
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
# 2.4 实验分析结论
# 2.4.1 效果对比实验
在 LOCOMO 数据集上对 Mem0 和 Mem0g 进行了评估,baseline包括多种现有的记忆增强系统。测试主要包括 单跳、多跳、开放域 和 时间推理 四种问题类型。
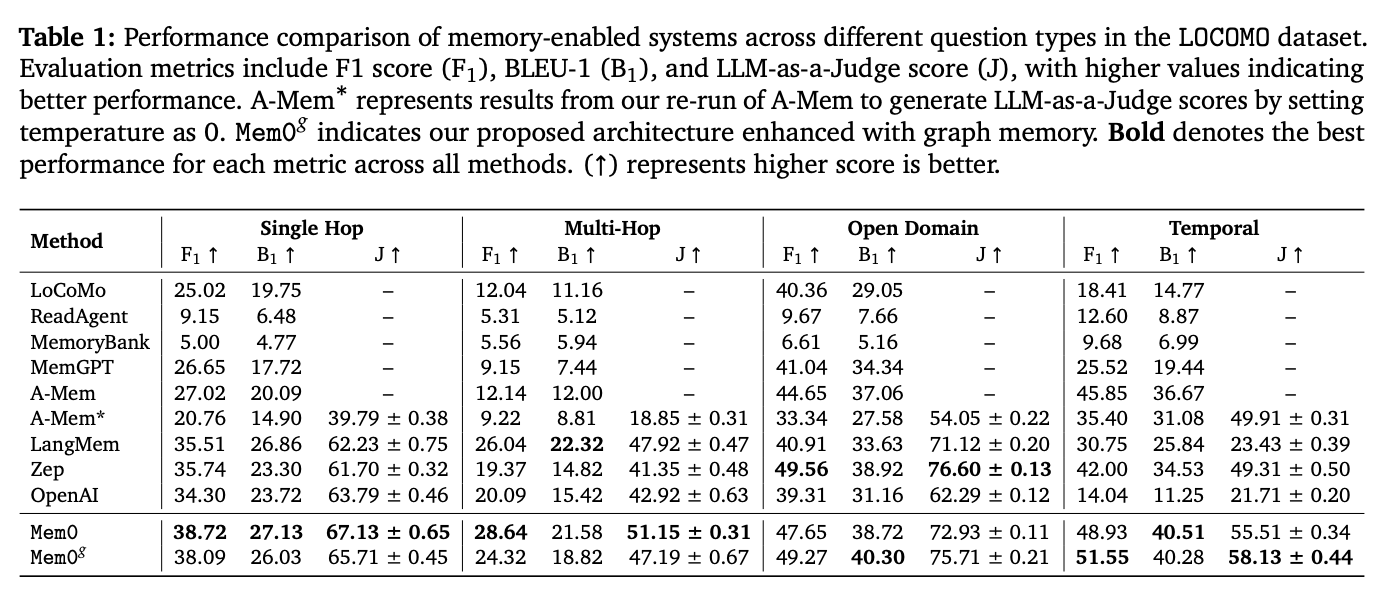
从上图可以看到,效果确实不错。但值得注意的一点是,用了知识图谱的方法并不一定比直接向量检索的方法好。
# 2.4.2 效率对比实验
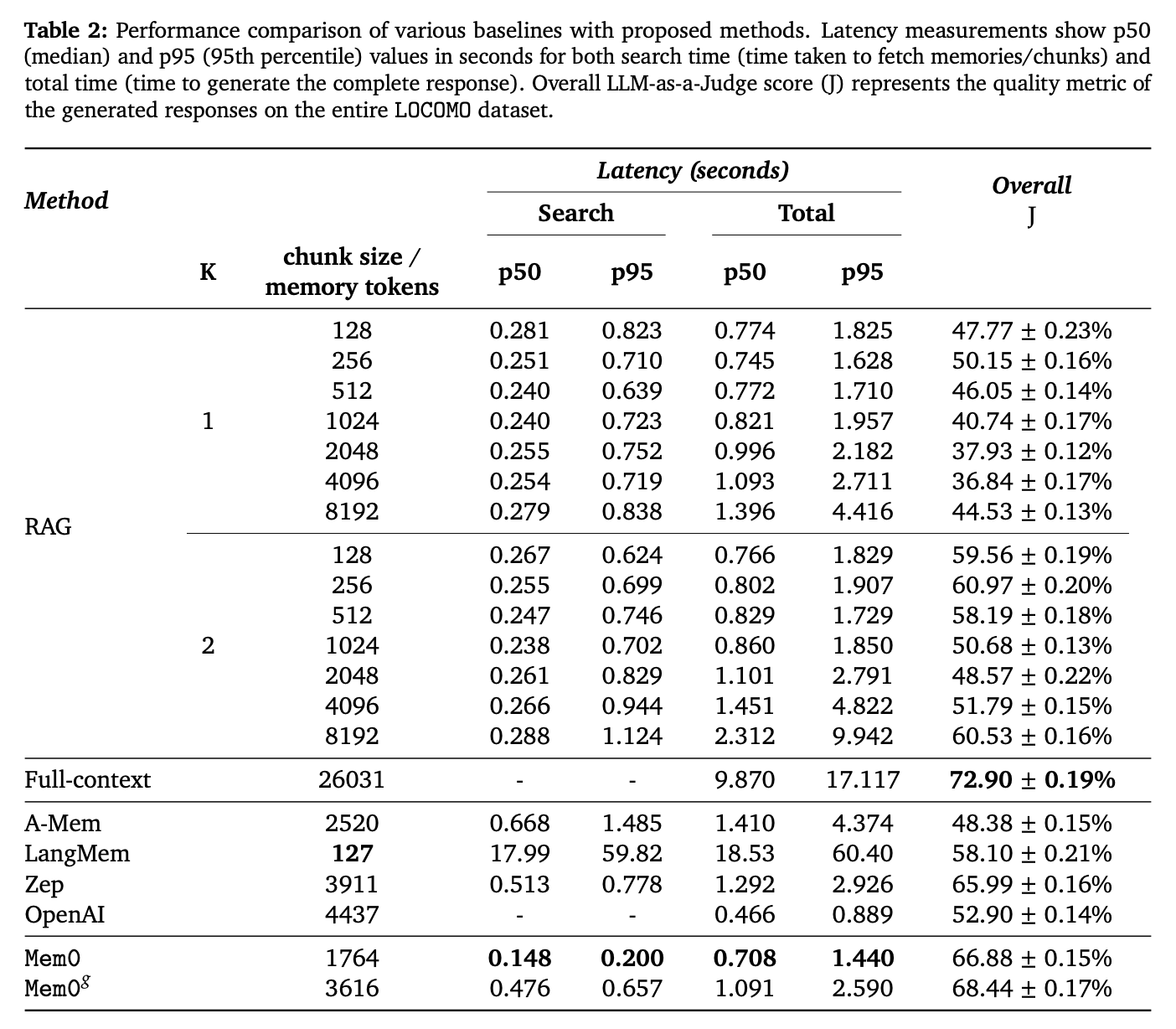
在计算效率方面,Mem0 和 Mem0g 都显著优于全上下文处理方法,尤其是在响应时间和 p95 上,二者分别减少了 91% 和 85% 的延迟。此外,Mem0g 在存储效率上略有增加,因为其图结构需要更多的内存空间。
# 3. Mem0使用实践
# 3.1 环境准备工作
[1] 准备依赖环境:这里使用 UV 来管理 Python 运行环境
$ uv venv .venv
$ source .venv/bin/activate
$ uv pip install "mem0ai" "openai>=1.35" "psycopg2-binary"
2
3
注:若安装的是 psycopg[binary] ,使用时会报错:ImportError: Neither 'psycopg' nor 'psycopg2' library is available. Please install one of them using 'pip install psycopg' or 'pip install psycopg2'.
[2] 准备LLM API:我这里选用了 OpenAI 的 gpt-4o-mini,全部支持详见:https://docs.mem0.ai/components/llms/overview (opens new window)
[3] 准备Embedding API:我这里选用了 OpenAI 的 text-embedding-3-small,一些常用的开源Embedding模型(如bge-m3)并没有做支持,全部支持详见:https://docs.mem0.ai/components/embedders/overview (opens new window)
[4] 准备向量检索库:我这里选用了Pgvector,全部支持情况详见 https://docs.mem0.ai/components/vectordbs/overview (opens new window)
注:新版 mem0 不再支持 sqlite 用作 vector_store,默认只支持向量数据库(如 pgvector、milvus、qdrant 等)。
# 3.2 Pgvector检索库
# 3.2.1 Pgvector简介
Pgvector 是一个强大的 PostgreSQL 扩展,它为 PostgreSQL 数据库添加了向量相似性搜索功能。
# 3.2.2 Pgvector部署
部署包目录结构:
.
├── build.sh
└── pgvector.zip // 提前从Github将pgvector的源码下载到这里(若缺失,脚本内会自动联网下载)
2
3
build.sh
#!/bin/bash
set -euo pipefail
# 配置项
POSTGRES_VERSION=17
CONTAINER_NAME=test_postgres
HOST_PORT=5432
DATA_VOLUME=pgdata
POSTGRES_USER=root
POSTGRES_PASSWORD='your_password'
POSTGRES_DB=postgres
BUSINESS_DB=test_postgres_db
PGVECTOR_ZIP=pgvector.zip
PGVECTOR_DIR=pgvector
PGVECTOR_URL=https://github.com/pgvector/pgvector/archive/refs/heads/master.zip
# 1. 拉取 PostgreSQL 镜像
docker pull postgres:${POSTGRES_VERSION}
# 2. 启动 PostgreSQL 容器
docker run -d \
--name "${CONTAINER_NAME}" \
--restart unless-stopped \
-e POSTGRES_USER="${POSTGRES_USER}" \
-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD="${POSTGRES_PASSWORD}" \
-e POSTGRES_DB="${POSTGRES_DB}" \
-e TZ=Asia/Shanghai \
-p "${HOST_PORT}:5432" \
-v "${DATA_VOLUME}":/var/lib/postgresql/data \
--health-cmd='pg_isready -U ${POSTGRES_USER}' \
--health-interval=10s \
--health-timeout=5s \
--health-retries=5 \
postgres:${POSTGRES_VERSION} \
-c max_connections=500
# 3. 安装构建 pgvector 所需依赖
docker exec "${CONTAINER_NAME}" apt update
docker exec "${CONTAINER_NAME}" apt install -y unzip git build-essential postgresql-server-dev-${POSTGRES_VERSION}
# 4. 下载并解压 pgvector.zip 到 pgvector 目录
if [ ! -d "${PGVECTOR_DIR}" ]; then
if [ ! -f "${PGVECTOR_ZIP}" ]; then
echo "未找到 ${PGVECTOR_ZIP},尝试自动下载..."
if ! wget "${PGVECTOR_URL}" -O "${PGVECTOR_ZIP}"; then
echo "自动下载失败,请手动执行以下命令:"
echo "wget ${PGVECTOR_URL} -O ${PGVECTOR_ZIP}"
exit 1
fi
fi
echo "正在校验 ${PGVECTOR_ZIP} 是否为有效 zip..."
if ! unzip -t "${PGVECTOR_ZIP}" > /dev/null 2>&1; then
echo "${PGVECTOR_ZIP} 不是有效的 zip 文件,请删除后重新执行脚本或手动下载。"
exit 1
fi
echo "正在解压 ${PGVECTOR_ZIP}..."
unzip -q "${PGVECTOR_ZIP}" -d temp_pgvector
mv temp_pgvector/pgvector-* "${PGVECTOR_DIR}"
rm -rf temp_pgvector
echo "解压完成,目录为:${PGVECTOR_DIR}"
fi
# 5. 编译安装 pgvector 插件
docker cp "./${PGVECTOR_DIR}" "${CONTAINER_NAME}":/tmp/pgvector
docker exec "${CONTAINER_NAME}" bash -c "cd /tmp/pgvector && make -j\$(nproc) && make install"
# 6. 初始化数据库
docker exec -it "${CONTAINER_NAME}" psql -U "${POSTGRES_USER}" -d "${POSTGRES_DB}" -c "CREATE DATABASE ${BUSINESS_DB};"
# 7. 启用 pgvector 插件
docker exec -it "${CONTAINER_NAME}" psql -U "${POSTGRES_USER}" -d "${BUSINESS_DB}" -c "CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector;"
# 8. 检查插件是否启用成功
echo "正在验证 pgvector 插件是否生效..."
docker exec -it "${CONTAINER_NAME}" psql -U "${POSTGRES_USER}" -d "${BUSINESS_DB}" -c "\dx" | grep vector \
&& echo "pgvector 插件已安装并启用" \
|| echo "pgvector 插件未安装成功"
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
# 3.3 Mem0记忆管理
Mem0入门使用详见:https://docs.mem0.ai/open-source/python-quickstart (opens new window)
# 3.3.1 运行示例脚本
我这里使用的是第三方 OpenAI 接口,因此配置了 OPENAI_BASE_URL。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import json
from typing import Optional, List, Any, Dict
from mem0 import Memory
OPENAI_API_KEY = "sk-xxx"
OPENAI_BASE_URL = "https://xxx.xxx.xxx/v1"
OPENAI_CHAT_MODEL = "gpt-4o-mini"
OPENAI_EMBED_MODEL = "text-embedding-3-small"
PG_CONN = "postgresql://root:[email protected]:5432/test_postgres_db"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = OPENAI_API_KEY
os.environ["OPENAI_BASE_URL"] = OPENAI_BASE_URL
def ensure_pgvector_extension(conn_str: str) -> None:
try:
try:
import psycopg
using = "psycopg"
conn = psycopg.connect(conn_str)
conn.autocommit = True
with conn.cursor() as cur:
cur.execute("CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector;")
cur.execute("SHOW server_version;")
ver = cur.fetchone()[0]
conn.close()
print(f"[检查数据库] 已确保安装 pgvector(驱动:{using},版本:{ver})")
except Exception:
import psycopg2
using = "psycopg2"
conn = psycopg2.connect(conn_str)
conn.autocommit = True
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector;")
cur.execute("SHOW server_version;")
ver = cur.fetchone()[0]
cur.close()
conn.close()
print(f"[检查数据库] 已确保安装 pgvector(驱动:{using},版本:{ver})")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[检查数据库] 跳过(无法连接或无驱动):{e}")
def pause(msg: str = "按回车继续..."):
try:
input(msg)
except EOFError:
pass
def pretty(title: str, data: Any):
print(f"\n=== {title} ===")
if isinstance(data, (dict, list)):
print(json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2))
else:
print(data)
def build_config() -> dict:
cfg = {
"llm": {
"provider": "openai",
"config": {
"model": OPENAI_CHAT_MODEL,
"api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"],
"openai_base_url": os.environ["OPENAI_BASE_URL"],
}
},
"embedder": {
"provider": "openai",
"config": {
"model": OPENAI_EMBED_MODEL,
"api_key": os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"],
"openai_base_url": os.environ["OPENAI_BASE_URL"],
}
},
"vector_store": {
"provider": "pgvector",
"config": {
"connection_string": PG_CONN
}
}
}
return cfg
def search_top_n(
m: Memory,
query: str,
user_id: str,
n: int = 3,
threshold: Optional[float] = None,
extra_filters: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
使用 mem0 内置的 limit/threshold/filters 做检索与截断。
- n: 结果条数上限
- threshold: 相似度阈值
- extra_filters: 额外过滤字段
"""
ef = dict(extra_filters or {})
ef.setdefault("user_id", user_id)
u = ef.get("user_id")
a = ef.get("agent_id")
r = ef.get("run_id")
filter_fields = {k: v for k, v in ef.items() if k not in ("user_id", "agent_id", "run_id")}
return m.search(
query=query,
user_id=u,
agent_id=a,
run_id=r,
limit=n,
filters=filter_fields if filter_fields else None,
threshold=threshold,
)
def find_most_relevant_id(m: Memory, query: str, user_id: str) -> Optional[str]:
"""基于查询从搜索结果中选出 Top1 的记忆 id(已用 limit=1 提速)。"""
res = m.search(query=query, user_id=user_id, limit=1)
if not isinstance(res, dict):
return None
items = res.get("results") or []
if not isinstance(items, list) or not items:
return None
top = items[0]
return getattr(top, "id", None) or top.get("id")
def update_most_relevant(m: Memory, user_id: str, query: str, new_text: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""先检索最相关记忆,再执行更新;若找不到则返回提示结构。"""
mem_id = find_most_relevant_id(m, query=query, user_id=user_id)
if not mem_id:
return {
"updated": False,
"reason": "未找到相关记忆,无法更新",
"query": query,
"new_text": new_text
}
updated = m.update(memory_id=mem_id, data=new_text)
return {"updated": True, "memory_id": mem_id, "result": updated}
def add(m: Memory, text: str, category: str, topic: str, user_id: str = "test_user") -> dict:
"""统一写入接口,便于批量添加与维护标签。"""
return m.add(text, user_id=user_id, metadata={"category": category, "topic": topic})
def bulk_add_memories(m: Memory, user_id: str = "test_user") -> List[dict]:
"""批量写入用于测试的记忆信息"""
R = []
# 基本画像与对话偏好
R.append(add(m, "我是软件开发人员,技术栈主要为Java与Python。", "profile", "skills", user_id))
R.append(add(m, "我平时常用的操作系统是macOS和Linux。", "profile", "os", user_id))
R.append(add(m, "除非我明确指定语言,否则默认使用中文进行回复与沟通。", "preference", "language", user_id))
# 提交规范与分支策略
R.append(add(m, "Git提交信息必须使用全英文、精炼;遵循类型:feat, fix, perf, refactor, docs, style, test, build, revert, ci, release, workflow, chore。", "preference", "git_commit", user_id))
R.append(add(m, "优先遵循Conventional Commits样式:type(scope): summary;禁止冗长标题,必要时在body补充。", "preference", "commit_convention", user_id))
R.append(add(m, "分支策略:main为受保护分支;功能以feature/*命名,修复以fix/*命名;通过PR合并并要求至少一次代码审查。", "preference", "branching", user_id))
# 脚本及代码规范
R.append(add(m, "Shell脚本风格:不使用表情;默认set -euo pipefail;显式声明bash;参数校验与错误信息友好。", "preference", "shell_style", user_id))
R.append(add(m, "Python风格:建议使用Black或Ruff进行格式化;必要时提供requirements.txt或pyproject.toml。", "preference", "python_style", user_id))
R.append(add(m, "Java风格:建议使用Maven或Gradle标准项目结构;提供可复现的构建命令。", "preference", "java_style", user_id))
# 依赖与容器化
R.append(add(m, "依赖管理偏好:固定版本、可复现构建,避免隐式全局依赖。", "preference", "deps_lock", user_id))
R.append(add(m, "Docker规范:尽量使用小体积基础镜像,多阶段构建", "preference", "docker_style", user_id))
return R
def dry_run_list(m: Memory,
user_id: Optional[str] = None,
agent_id: Optional[str] = None,
run_id: Optional[str] = None) -> dict:
"""
仅预览要删除的数量与部分 ID,避免误删。返回 {ok, count, ids}
"""
if not any([user_id, agent_id, run_id]):
return {"ok": False, "error": "必须至少提供一个过滤条件:user_id/agent_id/run_id"}
filters: Dict[str, Any] = {}
if user_id: filters["user_id"] = user_id
if agent_id: filters["agent_id"] = agent_id
if run_id: filters["run_id"] = run_id
listed = m.vector_store.list(filters=filters)
memories = listed[0] if isinstance(listed, (list, tuple)) and len(listed) == 2 else listed
ids = []
for x in memories[:20]:
mid = getattr(x, "id", None) or (x.get("id") if isinstance(x, dict) else None)
if isinstance(mid, str):
ids.append(mid)
count = len(memories)
return {"ok": True, "count": count, "ids": ids}
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("步骤 0:检查数据库 pgvector 扩展")
ensure_pgvector_extension(PG_CONN)
pause()
print("步骤 1:构建 Memory 实例")
config = build_config()
m = Memory.from_config(config)
print("[OK] Memory 初始化成功")
pause()
print("步骤 2:批量写入长期记忆")
write_results = bulk_add_memories(m, user_id="test_user")
pretty("批量写入结果", write_results)
pause()
print("步骤 3:拉取该用户全部记忆")
all_memories = m.get_all(user_id="test_user")
pretty("All", all_memories)
pause()
print("步骤 4:进行检索示例(内置 limit 控制条数)")
q1 = "提交信息和分支策略的要求是什么?"
related1 = search_top_n(m, query=q1, user_id="test_user", n=3)
pretty(f"Search: {q1}", related1)
q2 = "代码与脚本风格方面我有哪些偏好?"
related2 = search_top_n(m, query=q2, user_id="test_user", n=5, threshold=0.3)
pretty(f"Search: {q2}", related2)
pause()
print("步骤 5:基于检索更新最相关记忆(示例:在技能里补充Go)")
update_query = "我的开发技能与编程语言相关的记忆"
new_text = "我是软件开发人员,技术栈为 Java、Python,并且也会使用 Go。"
update_result = update_most_relevant(m, user_id="test_user", query=update_query, new_text=new_text)
pretty("UpdateMostRelevant", update_result)
pause()
if isinstance(update_result, dict) and update_result.get("updated"):
mem_id = update_result.get("memory_id")
print("步骤 6:查看该记忆的历史变更")
history = m.history(memory_id=mem_id)
pretty("History", history)
pause()
print("步骤 7:删除该记忆")
deleted = m.delete(memory_id=mem_id)
pretty("DeletedOne", deleted)
pause()
print("\n全部演示步骤完成。")
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
# 3.3.2 测试结果输出
步骤 0:检查数据库 pgvector 扩展
[检查数据库] 已确保安装 pgvector(驱动:psycopg,版本:17.5 (Debian 17.5-1.pgdg120+1))
按回车继续...
步骤 1:构建 Memory 实例
[OK] Memory 初始化成功
按回车继续...
步骤 2:批量写入长期记忆
=== 批量写入结果 ===
[
{
"results": [
{
"id": "d6b32ed3-1770-499c-9084-3b6734ef38c9",
"memory": "我是软件开发人员",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "8f0c3176-39dd-46f6-ad0b-615aa9253a76",
"memory": "技术栈主要为Java与Python",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "1a4ae05c-8ccc-44d5-b858-41d0c53d5dc6",
"memory": "平时常用的操作系统是macOS和Linux",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "fec0acc4-abc0-4045-ae8d-496f45ff1d24",
"memory": "默认使用中文进行回复与沟通",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "96be52dc-ec11-42aa-ad86-1d4c004f2dfb",
"memory": "Git提交信息必须使用全英文、精炼",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "34590e41-de44-48a1-bc19-1b36030aeb91",
"memory": "遵循类型:feat, fix, perf, refactor, docs, style, test, build, revert, ci, release, workflow, chore",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "e9324967-742c-48f9-94c2-bb697c1816c1",
"memory": "优先遵循Conventional Commits样式:type(scope): summary",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "a9038dfb-a223-4667-8a4a-700f66492c28",
"memory": "禁止冗长标题,必要时在body补充",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "00723671-0ce2-4b1f-93b4-d687360c84bc",
"memory": "分支策略:main为受保护分支",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "8ebc01d3-78e8-4289-a8ba-29ee6c920858",
"memory": "功能以feature/*命名",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "466fdb0d-be22-4efd-8058-15776c5d1f96",
"memory": "修复以fix/*命名",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "53b31627-5b16-4bb3-bc0b-c77569300726",
"memory": "通过PR合并并要求至少一次代码审查",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "8ab76820-03ed-4bc7-8f16-2ab21582613c",
"memory": "Shell脚本风格:不使用表情",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "3eb8a482-1330-491e-af85-eecf32b1c7c2",
"memory": "默认set -euo pipefail",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "84713ed1-a87c-4139-994a-3f096d4b7887",
"memory": "显式声明bash",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "2c6b6110-385c-4c3a-b23a-e544ab3fc65f",
"memory": "参数校验与错误信息友好",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "c7c70024-2e4e-4225-a296-eadb2d807330",
"memory": "建议使用Black或Ruff进行Python代码格式化",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "a03346fa-767c-4ae7-9c82-651280392a4a",
"memory": "必要时提供requirements.txt或pyproject.toml",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "c8379dd2-827f-4cac-af71-b29457c7ee19",
"memory": "建议使用Maven或Gradle标准项目结构",
"event": "ADD"
},
{
"id": "bb8095fa-9f21-4639-8799-53e3bdc58c38",
"memory": "提供可复现的构建命令",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "59a51f06-5ab2-46bd-8001-d41964deaac7",
"memory": "依赖管理偏好:固定版本、可复现构建,避免隐式全局依赖",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
},
{
"results": [
{
"id": "b26904ce-a72d-4b21-a401-d34ae6a26508",
"memory": "Docker规范:尽量使用小体积基础镜像,多阶段构建",
"event": "ADD"
}
]
}
]
按回车继续...
步骤 3:拉取该用户全部记忆
=== All ===
{
"results": [
{
"id": "d6b32ed3-1770-499c-9084-3b6734ef38c9",
"memory": "我是软件开发人员",
"hash": "1d6c1de4e61aa0461b3f1f71737e1c0a",
"metadata": {
"topic": "skills",
"category": "profile"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:19:52.324989-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "8f0c3176-39dd-46f6-ad0b-615aa9253a76",
"memory": "技术栈主要为Java与Python",
"hash": "40a057e828deb0b97f01976f9d3c6aac",
"metadata": {
"topic": "skills",
"category": "profile"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:19:53.533921-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "1a4ae05c-8ccc-44d5-b858-41d0c53d5dc6",
"memory": "平时常用的操作系统是macOS和Linux",
"hash": "f39c0ba68357cd11f6c1b672f96ea9e7",
"metadata": {
"topic": "os",
"category": "profile"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:16.114088-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "fec0acc4-abc0-4045-ae8d-496f45ff1d24",
"memory": "默认使用中文进行回复与沟通",
"hash": "8a27204d42a1be27f743c48a59e65a88",
"metadata": {
"topic": "language",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:25.118303-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "96be52dc-ec11-42aa-ad86-1d4c004f2dfb",
"memory": "Git提交信息必须使用全英文、精炼",
"hash": "942ed156c04511971b2d5868f3d80870",
"metadata": {
"topic": "git_commit",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:38.044437-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "34590e41-de44-48a1-bc19-1b36030aeb91",
"memory": "遵循类型:feat, fix, perf, refactor, docs, style, test, build, revert, ci, release, workflow, chore",
"hash": "e7f93127058f425e3936dd44237e6ce1",
"metadata": {
"topic": "git_commit",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:38.884790-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "e9324967-742c-48f9-94c2-bb697c1816c1",
"memory": "优先遵循Conventional Commits样式:type(scope): summary",
"hash": "350647624b269d8c01ed63d862903ad3",
"metadata": {
"topic": "commit_convention",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:52.269888-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "a9038dfb-a223-4667-8a4a-700f66492c28",
"memory": "禁止冗长标题,必要时在body补充",
"hash": "53002cf031c884ef48dc50c0e3ec10e1",
"metadata": {
"topic": "commit_convention",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:53.113855-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "00723671-0ce2-4b1f-93b4-d687360c84bc",
"memory": "分支策略:main为受保护分支",
"hash": "7680f2a98d970dfcfce10936bf27b8bd",
"metadata": {
"topic": "branching",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:11.668965-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "8ebc01d3-78e8-4289-a8ba-29ee6c920858",
"memory": "功能以feature/*命名",
"hash": "c35a9466604ea92b23cdf7a6a57d89ea",
"metadata": {
"topic": "branching",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:12.536842-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "466fdb0d-be22-4efd-8058-15776c5d1f96",
"memory": "修复以fix/*命名",
"hash": "87633e4fa1ee3473221d4708f75ec702",
"metadata": {
"topic": "branching",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:13.694794-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "53b31627-5b16-4bb3-bc0b-c77569300726",
"memory": "通过PR合并并要求至少一次代码审查",
"hash": "3a428c15350a2b5fdd85021cc51ff164",
"metadata": {
"topic": "branching",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:14.908130-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "8ab76820-03ed-4bc7-8f16-2ab21582613c",
"memory": "Shell脚本风格:不使用表情",
"hash": "181d4a6004309335151c45e9e85a98f1",
"metadata": {
"topic": "shell_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:33.106769-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "3eb8a482-1330-491e-af85-eecf32b1c7c2",
"memory": "默认set -euo pipefail",
"hash": "fb601ee67d5af4e1df6d4c6fc9945be2",
"metadata": {
"topic": "shell_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:33.956893-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "84713ed1-a87c-4139-994a-3f096d4b7887",
"memory": "显式声明bash",
"hash": "a79d298a2c09dc370b82281f48d48072",
"metadata": {
"topic": "shell_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:35.075166-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "2c6b6110-385c-4c3a-b23a-e544ab3fc65f",
"memory": "参数校验与错误信息友好",
"hash": "1420936b1c97faa52239ccff1154259c",
"metadata": {
"topic": "shell_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:37.525376-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "c7c70024-2e4e-4225-a296-eadb2d807330",
"memory": "建议使用Black或Ruff进行Python代码格式化",
"hash": "8d1f8b4cac74fa3bee9bd31e32a79dd7",
"metadata": {
"topic": "python_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:22:01.174565-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "a03346fa-767c-4ae7-9c82-651280392a4a",
"memory": "必要时提供requirements.txt或pyproject.toml",
"hash": "312afcade403598a7ec618639d8e5ead",
"metadata": {
"topic": "python_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:22:02.049682-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "c8379dd2-827f-4cac-af71-b29457c7ee19",
"memory": "建议使用Maven或Gradle标准项目结构",
"hash": "1045427205f9c98714500b518c7510f2",
"metadata": {
"topic": "java_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:22:50.869717-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "bb8095fa-9f21-4639-8799-53e3bdc58c38",
"memory": "提供可复现的构建命令",
"hash": "d2c49ae2eb1f39c3062d0af50cf724fb",
"metadata": {
"topic": "java_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:22:51.718389-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "59a51f06-5ab2-46bd-8001-d41964deaac7",
"memory": "依赖管理偏好:固定版本、可复现构建,避免隐式全局依赖",
"hash": "017c39ed40011f0700c13baff856327b",
"metadata": {
"topic": "deps_lock",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:23:02.064624-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "b26904ce-a72d-4b21-a401-d34ae6a26508",
"memory": "Docker规范:尽量使用小体积基础镜像,多阶段构建",
"hash": "e43767bede7e58be9ab2e451484768b4",
"metadata": {
"topic": "docker_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:23:18.482307-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
}
]
}
按回车继续...
步骤 4:进行检索示例(内置 limit 控制条数)
=== Search: 提交信息和分支策略的要求是什么? ===
{
"results": [
{
"id": "00723671-0ce2-4b1f-93b4-d687360c84bc",
"memory": "分支策略:main为受保护分支",
"hash": "7680f2a98d970dfcfce10936bf27b8bd",
"metadata": {
"topic": "branching",
"category": "preference"
},
"score": 0.546326531579298,
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:11.668965-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "e9324967-742c-48f9-94c2-bb697c1816c1",
"memory": "优先遵循Conventional Commits样式:type(scope): summary",
"hash": "350647624b269d8c01ed63d862903ad3",
"metadata": {
"topic": "commit_convention",
"category": "preference"
},
"score": 0.622262742125637,
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:52.269888-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "96be52dc-ec11-42aa-ad86-1d4c004f2dfb",
"memory": "Git提交信息必须使用全英文、精炼",
"hash": "942ed156c04511971b2d5868f3d80870",
"metadata": {
"topic": "git_commit",
"category": "preference"
},
"score": 0.6335021118524201,
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:38.044437-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
}
]
}
=== Search: 代码与脚本风格方面我有哪些偏好? ===
{
"results": [
{
"id": "8ab76820-03ed-4bc7-8f16-2ab21582613c",
"memory": "Shell脚本风格:不使用表情",
"hash": "181d4a6004309335151c45e9e85a98f1",
"metadata": {
"topic": "shell_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"score": 0.4512144385320618,
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:33.106769-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "c7c70024-2e4e-4225-a296-eadb2d807330",
"memory": "建议使用Black或Ruff进行Python代码格式化",
"hash": "8d1f8b4cac74fa3bee9bd31e32a79dd7",
"metadata": {
"topic": "python_style",
"category": "preference"
},
"score": 0.5630931816641572,
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:22:01.174565-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "e9324967-742c-48f9-94c2-bb697c1816c1",
"memory": "优先遵循Conventional Commits样式:type(scope): summary",
"hash": "350647624b269d8c01ed63d862903ad3",
"metadata": {
"topic": "commit_convention",
"category": "preference"
},
"score": 0.5872662663459749,
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:52.269888-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "34590e41-de44-48a1-bc19-1b36030aeb91",
"memory": "遵循类型:feat, fix, perf, refactor, docs, style, test, build, revert, ci, release, workflow, chore",
"hash": "e7f93127058f425e3936dd44237e6ce1",
"metadata": {
"topic": "git_commit",
"category": "preference"
},
"score": 0.6082115044341678,
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:20:38.884790-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
},
{
"id": "8ebc01d3-78e8-4289-a8ba-29ee6c920858",
"memory": "功能以feature/*命名",
"hash": "c35a9466604ea92b23cdf7a6a57d89ea",
"metadata": {
"topic": "branching",
"category": "preference"
},
"score": 0.6239359490890504,
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:21:12.536842-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"user_id": "test_user"
}
]
}
按回车继续...
步骤 5:基于检索更新最相关记忆(示例:在技能里补充Go)
=== UpdateMostRelevant ===
{
"updated": true,
"memory_id": "d6b32ed3-1770-499c-9084-3b6734ef38c9",
"result": {
"message": "Memory updated successfully!"
}
}
按回车继续...
步骤 6:查看该记忆的历史变更
=== History ===
[
{
"id": "8facf8d4-f749-4254-a638-38ba3a6d759f",
"memory_id": "d6b32ed3-1770-499c-9084-3b6734ef38c9",
"old_memory": null,
"new_memory": "我是软件开发人员",
"event": "ADD",
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:19:52.324989-07:00",
"updated_at": null,
"is_deleted": false,
"actor_id": null,
"role": null
},
{
"id": "0d0a0756-8fb4-4932-9c33-cb691f902d7a",
"memory_id": "d6b32ed3-1770-499c-9084-3b6734ef38c9",
"old_memory": "我是软件开发人员",
"new_memory": "我是软件开发人员,技术栈为 Java、Python,并且也会使用 Go。",
"event": "UPDATE",
"created_at": "2025-06-21T20:19:52.324989-07:00",
"updated_at": "2025-06-21T20:43:47.465974-07:00",
"is_deleted": false,
"actor_id": null,
"role": null
}
]
按回车继续...
步骤 7:删除该记忆
=== DeletedOne ===
{
"message": "Memory deleted successfully!"
}
按回车继续...
全部演示步骤完成。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
# 4. 记忆相关概念区分
# 4.1 自定义指令与长期记忆
自定义指令是由用户主动输入并长期固定存在的规则,通常作为全局设定传递;长期记忆则由系统根据历史会话交互自动提取,可随对话演变更新。二者在调用时的传递方式相同,都是注入到模型输入中,但在来源、更新机制和生命周期上存在差异。
| 对比维度 | 自定义指令(Custom Instructions) | 长期记忆(Memory) |
|---|---|---|
| 产生方式 | 用户主动输入 | 系统从历史对话提取 / 用户编辑 |
| 变化频率 | 固定,不随对话变化 | 动态,随对话和时间更新 |
| 作用时长 | 长期稳定存在,直到用户修改 | 按需检索,可能随时间衰减/合并 |
| 更新方式 | 仅用户显式修改 | 自动抽取写入或人工编辑 |
| 传递位置 | 每次调用拼接到 system | 每次调用前检索+压缩,注入到 system |
| 优先级 | 更高,作为稳定规则 | 可被任务临时覆盖,需做冲突调和 |
| 典型用途 | 全局风格/角色设定(语言、格式要求) | 个性化信息、历史事实(偏好、身份、上下文) |
# 4.2 短期记忆与长期记忆
短期记忆如同 RAM,负责保存当前会话上下文,保障对话连贯,但随会话结束即清空;长期记忆则类似 SSD,跨会话持久保存用户偏好、任务进度和知识点,并可在后续交互中检索注入。两者协同,使 Agent 既具备即时对话的流畅性,又能保持长期交互的一致性。
| 对比维度 | 短期记忆(工作记忆 / RAM) | 长期记忆(全局记忆 / SSD) |
|---|---|---|
| 功能定位 | 维持当前对话的内容连贯 | 跨会话保存信息 |
| 典型内容 | 最近对话、摘要 | 习惯偏好、用户身份 |
| 存储方式 | 上下文/缓存 | 数据库/向量库 |
| 生命周期 | 会话结束清空 | 长期持久保存 |
| 访问速度 | 快速直接 | 检索调用 |
| 应用场景 | 多轮连续对话 | 个性化问答 |
| 特点类比 | RAM(速度快、容易丢失) | SSD(容量大、存储持久) |
# 5. 参考资料
[2] 使用高效记忆算法将token减少40%以降低LLM的API成本 from 知乎 (opens new window)
[3] Mem0论文及源码解读:给你的大模型加上长期记忆 from 知乎 (opens new window)
[4] 深入浅出分析最近火热的Mem0个性化AI记忆层 from 博客园 (opens new window)
[5] Mem0快速入门 from 官方文档 (opens new window)
[6] Mem0基本介绍 from 官方文档 (opens new window)
[7] Mem0 的 REST API Server from 官方文档 (opens new window)
[9] 让AI Agent能记住用户偏好:mem0源码分析 from 知乎 (opens new window)
[10] 首次全面复盘AI Agents记忆系统:3大类,6种操作 from 知乎 (opens new window)
[11] 当LangGraph遇上Mem0:如何让你的AI Agent具有更智能的记忆与个性化的体验?from 火山引擎 (opens new window)